The Silent Battle with Leprosy
Leprosy, a disease shrouded in stigma and misconceptions, has been a part of human history for millennia. Despite significant medical advances leading to an effective leprosy cure, the battle for complete recovery often extends beyond the medical treatment. This article delves into the journey of a leprosy cured person, highlighting the physical, psychological, and social challenges they face in the quest for a full recovery.
Understanding Leprosy
Historical Context of Leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen’s disease, has been documented for thousands of years. Historically, those afflicted were often ostracized, living in isolated colonies. The fear and misunderstanding surrounding the disease contributed to its infamy.
Causes and Transmission
Leprosy is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae. It primarily affects the skin, nerves, respiratory tract, and eyes. The transmission occurs through prolonged close contact with an untreated infected person, usually via respiratory droplets.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of leprosy include discolored skin patches, numbness, muscle weakness, and eye problems. Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical examination and laboratory tests, including skin biopsies and smears.
The Journey to a Leprosy Cure
Historical Treatments and Breakthroughs
Early treatments for leprosy were largely ineffective and included herbal remedies and isolation. The significant breakthrough came in the mid-20th century with the development of antibiotics, notably dapsone.
Modern Medical Advances
Today, leprosy is treated effectively with multidrug therapy (MDT), a combination of antibiotics including dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine. This regimen, endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO), has been instrumental in reducing the global leprosy burden.
The Role of Multidrug Therapy (MDT)
MDT has revolutionized leprosy treatment, offering a reliable cure and preventing the spread of the disease. Patients typically complete treatment within 6-12 months, after which they are considered cured. However, the physical and emotional scars often linger.
The Life of a Leprosy Cured Person
Physical Recovery Challenges
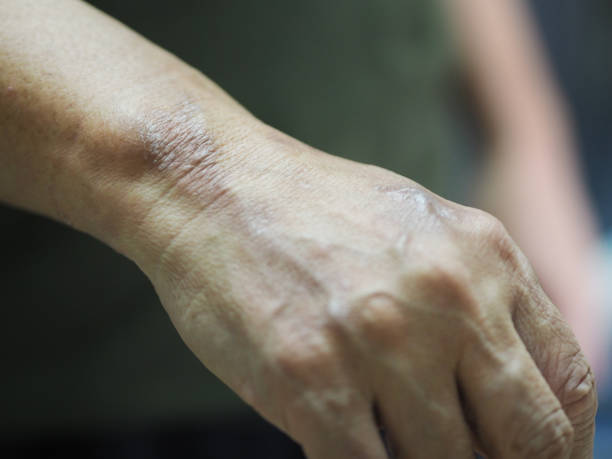
Even after a cure, many individuals experience lingering physical disabilities due to nerve damage caused by the disease. These can include loss of sensation, muscle weakness, and deformities, particularly in the hands and feet.
Psychological and Social Impacts
The stigma associated with leprosy can lead to significant psychological distress. Cured individuals may face discrimination, impacting their self-esteem and social interactions.
Stories of Resilience and Hope
Many leprosy survivors show incredible resilience, finding ways to overcome their disabilities and reclaim their lives. These stories of courage and determination offer hope and inspiration to others facing similar challenges.
Leprosy Cured Disability
Understanding Disabilities Post-Leprosy
Disabilities resulting from leprosy are primarily due to nerve damage. This can result in the loss of sensation and muscle control, leading to injuries and infections that can cause further complications.
Rehabilitation and Therapy
Rehabilitation is crucial for leprosy survivors to regain as much function as possible. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and sometimes surgical interventions are part of the comprehensive care needed.
Support Systems and Resources
Access to support systems, including counseling, peer support groups, and vocational training, is vital for the rehabilitation and reintegration of leprosy survivors. Various NGOs and health organizations provide these essential services.
One Woman’s Story
Her Battle with the Disease
In this section, we follow the journey of a woman who overcame leprosy. Diagnosed in her early twenties, she faced the daunting challenge of confronting a disease that carried not just physical but also social burdens.
The Treatment Journey
Her treatment journey was long and arduous. Starting with the initial shock of diagnosis, she navigated the complexities of MDT, dealing with side effects and the slow path to recovery.
Overcoming Physical Disabilities
Post-treatment, she confronted the physical disabilities that leprosy had left behind. Through intensive rehabilitation, she worked tirelessly to regain mobility and independence.
Dealing with Social Stigma
Social stigma was a significant hurdle. She faced discrimination in her community and workplace, but through advocacy and education, she began to change perceptions and build a supportive network.
The Road to Emotional Healing
Emotional healing was perhaps the most challenging aspect. With the help of counseling and support groups, she learned to cope with her experiences and found the strength to move forward.
The Global Fight Against Leprosy
Current Statistics and Trends
Despite the availability of a cure, leprosy remains a global health concern, particularly in developing countries. According to the WHO, there are still hundreds of thousands of new cases reported annually.
Ongoing Research and Development
Research continues to focus on better understanding the disease, improving treatments, and ultimately finding ways to prevent it. Advances in genetic studies and vaccine development hold promise for the future.
Organizations Making a Difference
Numerous organizations are dedicated to the eradication of leprosy and the support of those affected. These include the WHO, The Leprosy Mission, and the American Leprosy Missions, among others.
Living with the Scars
Coping Mechanisms and Strategies
Living with the scars of leprosy involves developing coping strategies to deal with both physical and emotional challenges. This can include regular medical check-ups, physical therapy, and participation in support groups.
Community Support and Advocacy
Community support plays a crucial role in the reintegration of leprosy survivors. Advocacy efforts aim to reduce stigma, promote understanding, and ensure access to necessary resources and support.
FAQs
What are the long-term effects of leprosy even after being cured?
Long-term effects can include nerve damage, muscle weakness, and disabilities. Emotional and social impacts due to stigma are also significant.
Can disabilities caused by leprosy be fully rehabilitated?
While some disabilities can be significantly improved with rehabilitation, complete recovery may not always be possible. Early treatment and ongoing therapy are crucial.
What support is available for leprosy cured individuals?
Support includes medical care, rehabilitation services, counseling, vocational training, and peer support groups. Various organizations provide these resources.
How does social stigma affect leprosy survivors?
Social stigma can lead to discrimination, isolation, and psychological distress. It can affect survivors’ ability to find work, maintain relationships, and integrate into society.
What are the signs that leprosy treatment is working?
Signs of effective treatment include the cessation of new lesions, reduction in symptoms, and the prevention of disease spread. Regular follow-up is essential to monitor progress.
How can communities help leprosy survivors reintegrate?
Communities can help by promoting awareness and understanding, providing support and resources, and advocating for the rights of leprosy survivors.
Conclusion
A Message of Hope and Resilience
Leprosy, once a feared and misunderstood disease, is now curable. However, the journey to complete recovery involves addressing the physical, emotional, and social scars left behind. Through resilience, support, and advocacy, leprosy survivors can reclaim their lives and inspire others with their stories of courage and determination.